The Alarming Rise of Overweight and Obesity
This year, a report reveals a staggering truth: about 34.8% of the studied Chinese population is overweight, and 14.4% is obese. In terms of gender, it is observed that around 41.1% of studied males is overweight or obese, while the proportion for females stands at 27.7%. Globally, in 2016, the number of overweight adults surpassed 1.9 billion, with over 650 million were. The World Health Organization states that worldwide obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, showing a worrying picture.

How to tell overweight and obesity
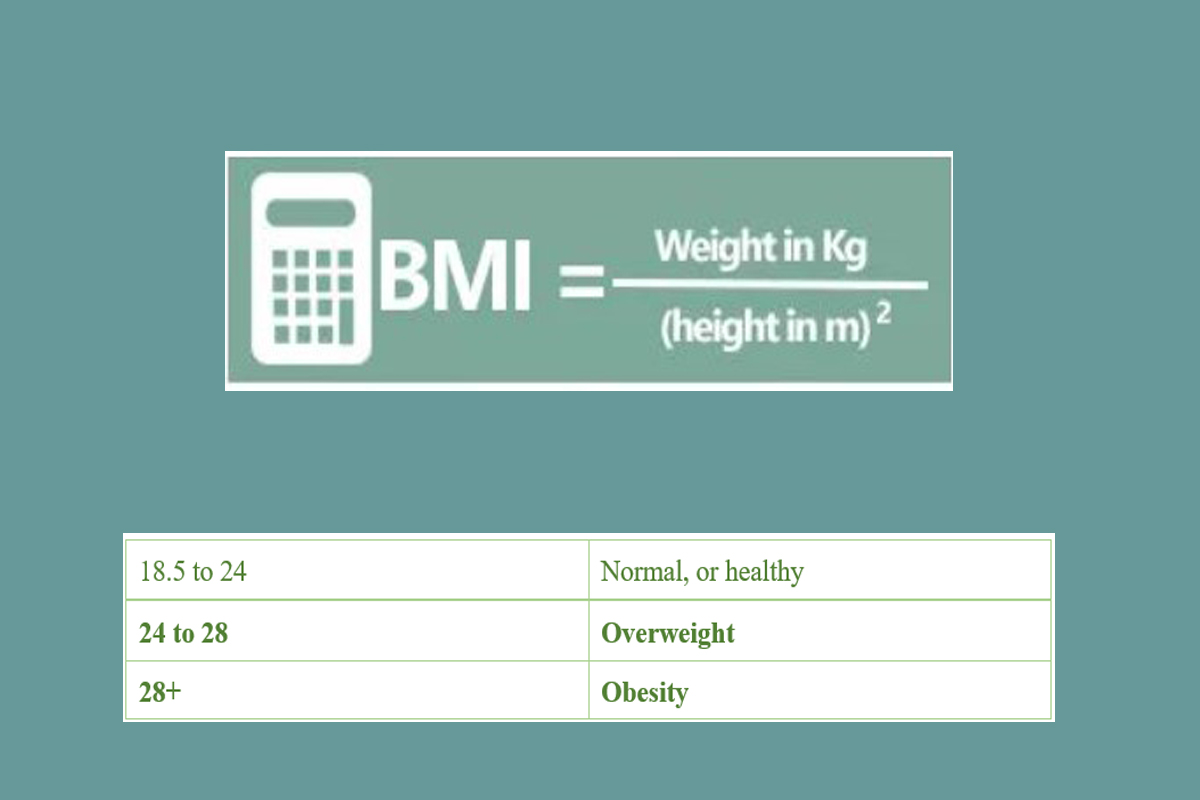
BMI is a tool to estimate and screen for overweight and obesity, defined as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. It is related to the amount of fat in your body. A high amount of fat can raise the risk of many health problems.
The table below shows BMI standerds:
What causes obesity and overweight?
The underlying cause lies in the imbalance between calorie intake and expenditure, where intake often exceeds expenditure. Psychological factors also play a role. Specifically, the reasons are as follows:
- Unhealthy eating habits: High consumption of fatty foods and sugary beverages.
- Lack of physical activity: Sedentary lifestyles during work hours and minimal activity after returning home.
- Excessive stress and negative emotions: Such as anger and anxiety, can result in increased secretion of adrenal corticosteroids. These hormones counteract insulin and contribute to the accumulation of abdominal fat.
What are common health consequences of overweight and obesity?
- 脂肪肝(zhī fáng gān) fatty liver disease
- 糖尿病(táng niào bìng) diabetes
- 血脂异常(xuè zhī yì cháng) dyslipidemia
The above are commonly associated with overweight and obesity. The incidence of fatty liver, is six times higher than those with a normal BMI. Besides, diabetes and dyslipidemia occur at twice the rate in obese individuals. Other potential health problems include:
- 心血管疾病(xīn xuè guǎn jí bìng )cardiovascular diseases: 高血压(gāo xuè yā)hypertension、脑血栓(nǎo xuè shuān ) cerebral thrombosis,心脏病(xīn zāng bìng)heart disease,中风(zhòng fēng) stroke. These mainly stem from the excessive accumulation of fat, which burdens the heart or raises blood pressure.
- 癌症(ái zhèng) cancer: 乳腺癌(rǔ xiàn ái) breast cancer、肝癌(gān ái) liver cancer、胆囊癌(dǎn náng ái) gallbladder cancer、肾癌(shèn ái) kidney cancer, 结肠癌(jié cháng ái) colon cancer。Excessive fat can adversely affect cell function.
- 消化系统疾病(xiāo huà xì tǒng jí bìng)digestive system diseases: 消化不良(xiāo huà bú liáng) indigestion 胃食管反流(wèi shí guǎn fǎn liú) gastroesophageal reflux.
- 睡眠呼吸暂停综合症(shuì mián hū xī zàn tíng zōng hé zhèng) sleep apnea syndrome: Obesity can lead to respiratory obstruction, causing asphyxia and cerebral hypoxia.
- 骨关节炎(gǔ guān jiē yán) osteoarthritis:Obesity places additional stress on the joints, leading to inflammation.
- 皮肤病(pí fū bìng) dermatological diseases:皮炎(pí yán) dermatitis、湿疹(shī zhěn) eczema。Weakened peripheral circulation in obese individuals can reduce the skin's resistance.
- 心理疾病(xīn lǐ jí bìng ) psychological disorders:社交恐惧症(shè jiāo kǒng jù zhèng) social phobia,抑郁(yì yù) depression.
How can overweight and obesity be reduced?
- Limit energy intake and eat rich in fruit, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and nuts
- Engage in regular physical activity (150 minutes spread through the week for adults).
- Keep cheerful. (Try to cultivate hobbies or engaging in activities that bring relaxation, such as singing, listening to music, watching movies, or playing basketball.)
Want to learn more medical vocabulary and medical related content? Come and book one of our one-on-one medical courses.